Introduction
Aluminum is one of the most popular metals used in machining, thanks to its lightweight, strength, and versatility. Whether you’re building components for the automotive, aerospace, or manufacturing industries, choosing the right aluminum alloy is crucial for achieving high-quality results. This guide will explore the different types of aluminum alloys, their properties, and why certain alloys like 6061 and 7075 are considered the best for machining. So, what exactly makes aluminum the go-to metal for machining projects? Let’s dive into this comprehensive guide and find out.
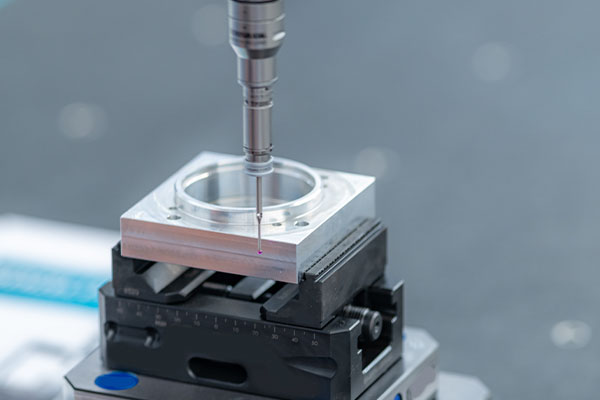

1. What is the Best Aluminum for Machining?
When choosing the best aluminum for machining, you need to consider the specific requirements of your project. So, what’s the real story? It’s not just about strength or durability; factors like machinability, cost, and resistance to corrosion play a huge role in deciding the right alloy for your application. Aluminum alloys come in a range of grades, each suited to different tasks.
6061 aluminum is often regarded as the go-to alloy for most machining projects because of its excellent machinability and good mechanical properties. But it’s not the only option. For high-strength applications, you might consider 7075 aluminum, which is favored in aerospace and military industries. But here’s the kicker: while 7075 is incredibly strong, it’s also more challenging to machine than 6061, and it comes at a higher cost.
Aluminum alloys like 2024 and 5083 also offer specific advantages, such as superior resistance to corrosion or high strength for aviation applications. So how do you pick the best aluminum for your machining needs? Let’s explore the characteristics and benefits of different alloys in detail.
Table: Common Aluminum Alloys and Their Applications
| Alloy | Strength | Machinability | Cost | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | Medium | Easy | Medium | Automotive, General Purpose |
| 7075 | High | Difficult | High | Aerospace, Military |
| 2024 | High | Moderate | Medium | Aircraft, High-stress parts |
| 5083 | Medium | Moderate | High | Marine, Marine environments |
| 1050 | Low | Easy | Low | Electrical components, Heat exchangers |
2. What Are the Most Popular Types of Aluminum Alloys?
Aluminum alloys come in different grades, each with its own set of characteristics. Ready for the good part? Let’s break down the most popular aluminum alloys used in machining: 6061, 7075, 2024, 5083, and 1050.
6061 Aluminum: The All-Purpose Workhorse
6061 aluminum is one of the most commonly used alloys in the industry. It’s prized for its excellent machinability, medium strength, and good resistance to corrosion. Why is 6061 so widely used? It offers a good balance of strength and flexibility, making it perfect for a wide range of applications, including automotive, construction, and marine.
7075 Aluminum: The Heavyweight Champion
If you need high strength, especially for aerospace or military applications, 7075 aluminum is your best bet. This alloy is known for its strength-to-weight ratio and is often used in parts that must withstand high-stress environments. But here’s the kicker: despite its strength, 7075 is harder to machine, which can lead to higher costs.
2024 Aluminum: The Aerospace Standard
2024 aluminum is another high-strength alloy, often used in aerospace applications. It’s not as versatile as 6061, but its strength makes it ideal for the aviation industry, where high-performance components are a must.
5083 Aluminum: Marine-Grade Excellence
5083 aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion, especially in marine environments. What’s the real story here? This makes it ideal for boat hulls, shipbuilding, and offshore structures, where saltwater exposure is constant.
1050 Aluminum: A Specialist Alloy
1050 aluminum is not as strong as 6061 or 7075, but it’s an excellent choice for applications where high electrical conductivity is required, such as in heat exchangers and electrical components. Its low strength makes it easier to machine, but it still offers good corrosion resistance.
Table: Aluminum Alloys Overview
| Alloy | Strength | Machinability | Resistance to Corrosion | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | Medium | Easy | Good | Automotive, Structural parts |
| 7075 | High | Difficult | Fair | Aerospace, Military |
| 2024 | High | Moderate | Fair | Aerospace, Aircraft |
| 5083 | Medium | Moderate | Excellent | Marine, Shipbuilding |
| 1050 | Low | Easy | Good | Electrical, Heat exchangers |
3. Why is 6061 Aluminum Considered the Best Choice for Machining?
6061 aluminum is widely considered one of the best choices for machining, and for good reason. This is where it gets interesting: its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of machining make it a go-to for manufacturers around the world.
The alloy is made from aluminum, magnesium, and silicon, which gives it a unique combination of strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance. 6061 is relatively easy to weld, and it can be heat-treated to increase its strength. So, what makes it the go-to alloy for machining? Its balance of properties makes it ideal for a wide range of industries, from automotive to aerospace. The alloy’s moderate strength allows it to handle heavy loads without being overly heavy, while its corrosion resistance ensures that it can stand up to the elements.
Table: Why 6061 Aluminum is Ideal for Machining
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Strength | Suitable for structural parts |
| Machinability | Easy to machine with standard tools |
| Corrosion Resistance | Ideal for outdoor and marine applications |
| Weldability | Can be welded without compromising strength |
| Cost | More affordable than high-strength alloys |
4. How Does Aluminum Alloy 7075 Perform in Machining?
Aluminum alloy 7075 is one of the strongest alloys available, but here’s the kicker: it’s harder to machine than other aluminum alloys like 6061. That’s because the alloy contains zinc, which increases strength but also makes it more difficult to work with.
7075 aluminum is often used in high-stress applications such as aerospace components, military equipment, and bicycle frames. Why is it so highly valued? It has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it perfect for applications that require both strength and lightness. However, its high strength also means it’s more prone to tool wear, and machining it requires specialized equipment.
Table: Aluminum Alloy 7075 Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Strength | Very High |
| Machinability | Difficult |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, Military, High-performance bikes |
5. What Are the Benefits of Machining 2024 Aluminum?
2024 aluminum is renowned for its strength, making it the preferred choice for aircraft and aerospace applications. You might be wondering: what makes 2024 such a powerhouse? The high strength of this alloy makes it ideal for parts that must endure extreme stresses and strains. Its tensile strength is higher than that of 6061, making it perfect for high-performance components.
However, 2024 aluminum does have its downsides. What’s the catch? It’s not as resistant to corrosion as 6061, so it may require additional treatments or coatings to protect it from environmental damage. Despite this, it’s still widely used in industries that require maximum strength.
Table: 2024 Aluminum vs. 6061 Aluminum
| Alloy | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | High | Moderate | Aircraft, Military |
| 6061 | Medium | Good | General purpose, Automotive |
6. What Makes 5083 Aluminum Ideal for Marine and Corrosive Environments?
When it comes to applications in marine environments, this is where it gets interesting: 5083 aluminum stands out for its superior resistance to corrosion. This property makes it a go-to choice for the construction of ships, offshore structures, and other marine equipment. 5083 aluminum is primarily known for its exceptional performance in environments where saltwater exposure is a constant concern.
One of the standout features of 5083 aluminum is its ability to resist corrosion caused by seawater, making it a perfect fit for maritime applications. Why is this so important? Without this level of resistance, aluminum would degrade quickly, leading to premature failures and costly repairs. The alloy also offers excellent weldability, which is a must in marine construction. This ensures that the material can be easily joined together during the manufacturing process, without compromising its strength or durability.
While 5083 aluminum is a great choice for marine environments, it is also used in other industries that deal with corrosive conditions, such as chemical plants and waste treatment facilities. But here’s the kicker: due to its corrosion resistance and specialized properties, 5083 aluminum can come at a higher price compared to alloys like 6061.
Table: Marine-Grade Aluminum 5083 Features
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to saltwater corrosion |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio |
| Weldability | Easily welded for large constructions |
| Common Applications | Shipbuilding, offshore platforms |
| Cost | Higher than general-purpose alloys |
7. What Are the Characteristics of 1050 Aluminum for Machining?
1050 aluminum is often overlooked, but you might be wondering why it’s still relevant in certain machining projects. This alloy is best known for its high electrical and thermal conductivity. Unlike some of the other alloys we’ve discussed, 1050 is relatively low in strength, but its exceptional conductivity makes it ideal for applications in electrical components and heat exchangers.
The alloy’s low strength means it’s not the best choice for high-stress components, but it’s perfect when you need an aluminum that can handle electrical currents or efficiently dissipate heat. What’s the catch? While it’s easy to machine, its low strength limits its use in applications that require structural integrity. However, its high corrosion resistance ensures it performs well in outdoor environments, making it useful in industries like HVAC, electrical wiring, and power generation.
Because 1050 aluminum is so easy to machine, it’s a favorite among manufacturers who need to quickly produce large quantities of parts. So, what are its limitations? Its lack of strength and hardness can be a drawback in certain applications, but in the right situation, it’s a highly effective material.
Table: Properties of 1050 Aluminum
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Strength | Low |
| Electrical Conductivity | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good |
| Machinability | Easy |
| Common Applications | Electrical components, heat exchangers |
8. What Should You Look for When Choosing Aluminum for Machining?
When choosing aluminum for machining, there are several factors you need to take into account to ensure the material meets your specific needs. This is where it gets interesting: it’s not just about the metal’s mechanical properties. You also need to consider factors like cost, availability, and environmental conditions.
First, you need to evaluate the strength of the aluminum. Are you creating parts that need to withstand high stress or heavy loads? If so, you’ll want to opt for high-strength alloys like 7075 or 2024. For general-purpose machining, however, alloys like 6061 provide the perfect balance of strength and machinability.
Next, machinability is a key consideration. Some aluminum alloys are easier to machine than others, so understanding how easily a material can be cut, drilled, or shaped is critical for optimizing production time and reducing costs. What’s the real story here? The better the machinability, the quicker and cheaper the project will be.
Lastly, you should also consider cost and availability. Alloys like 6061 tend to be more cost-effective and widely available, making them the go-to choice for many industries. High-strength alloys, on the other hand, tend to be more expensive and less readily available, so budget constraints may influence your decision.
Table: Factors to Consider When Choosing Aluminum for Machining
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Strength | Choose based on the application’s stress needs |
| Machinability | Opt for alloys that offer ease of machining |
| Cost | Balance strength and machinability with cost |
| Availability | Widely available alloys are easier to source |
9. How Do You Machine Different Aluminum Alloys?
Machining aluminum involves several processes, including cutting, drilling, and milling. However, the process can vary depending on the alloy being used. Ready for the good part? Let’s explore how machining differs for various aluminum alloys, particularly in terms of their hardness, strength, and machinability.
6061 aluminum is one of the easiest alloys to machine, making it the most popular choice in the industry. What’s the real story? It’s forgiving, and you can use standard tools and techniques for cutting, shaping, and finishing it.
7075, on the other hand, is much harder and stronger, which means it requires specialized equipment to machine effectively. The cutting speeds for 7075 are generally slower, and tool wear is more significant. So, while it can achieve high precision, it also comes at a higher cost.
2024 aluminum, with its high strength but moderate machinability, requires more attention to the cutting process. But here’s the kicker: while it’s harder to machine, its exceptional strength makes it worth the extra effort for certain high-performance applications.
Table: Machining Considerations for Different Aluminum Alloys
| Alloy | Machinability | Tools Needed | Cutting Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | Easy | Standard tools | High |
| 7075 | Difficult | Specialized tools | Low |
| 2024 | Moderate | Standard to advanced tools | Moderate |
| 5083 | Moderate | Standard tools | Moderate |
| 1050 | Easy | Standard tools | High |
10. How Do Aluminum Alloys Compare to Other Metals in Machining?
Aluminum is often favored in machining for its light weight, good strength, and machinability. What’s the catch, though? How does it stack up against other metals like steel, copper, and brass? Let’s compare aluminum alloys with these metals to see where they shine and where they fall short.
Aluminum has a distinct advantage over steel in terms of weight. But here’s the kicker: while steel is stronger, aluminum is much lighter, which makes it ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as in the aerospace industry. Copper, on the other hand, excels in electrical conductivity, but it’s more expensive and less commonly used in machining compared to aluminum.
Brass, while easier to machine than steel, doesn’t have the same strength-to-weight ratio as aluminum, making it less suited for structural applications. So, while aluminum might not be the best choice in every situation, it’s often the go-to metal due to its balance of properties.
Table: Aluminum vs. Other Metals for Machining
| Metal | Strength | Machinability | Weight | Cost | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Medium | Easy | Light | Medium | Automotive, Aerospace |
| Steel | High | Difficult | Heavy | Low | Structural components |
| Copper | Medium | Moderate | Heavy | High | Electrical components |
| Brass | Low | Easy | Medium | Medium | Decorative, Plumbing |
11. What Are Common Challenges When Machining Aluminum?
Machining aluminum presents unique challenges, particularly when it comes to handling the material’s tendency to create chips and heat buildup. So, what’s the deal here? The lightweight nature of aluminum means that chips can easily get caught in the cutting tools, leading to tool wear and production delays.
Aluminum also conducts heat better than other metals, which can lead to increased temperatures during machining. What’s the catch? Higher temperatures can cause thermal expansion, leading to warping or changes in the dimensions of your parts. To prevent this, using coolants and taking regular breaks during the machining process can help.
Another common challenge is cutting tool wear. Aluminum is relatively soft, but certain alloys, like 7075, can still cause significant wear on tools. This is where it gets interesting: using high-quality tools and optimizing machining parameters can reduce wear and extend tool life.
Table: Common Machining Challenges for Aluminum
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Chip buildup | Use chip breakers and coolant |
| Heat buildup | Optimize cutting speed and use coolant |
| Tool wear | Use coated tools and proper tool geometry |
| Warping or distortion | Use low cutting speeds and coolants |
12. How Can You Optimize Aluminum Machining for Better Results?
Optimizing aluminum machining is key to achieving high-quality results while minimizing waste and downtime. Ready for the good part? By adjusting cutting speeds, choosing the right tools, and implementing proper coolant systems, you can greatly improve the efficiency and quality of your machining projects.
First, make sure you’re using the right cutting tools. High-speed steel (HSS) tools may work for some alloys, but for tougher materials like 7075, carbide tools are necessary. What’s the catch? Carbide tools tend to last longer and maintain precision even at higher speeds.
So, what about cutting speeds? Increasing the cutting speed can help improve productivity, but it also generates more heat. But here’s the kicker: the optimal cutting speed will vary depending on the specific alloy you’re working with, so you’ll need to experiment to find the ideal settings.
Coolant is another critical factor. Using coolant not only helps to reduce temperatures but also flushes away chips and debris, ensuring smoother operations.
Table: Optimizing Machining Parameters for Aluminum
| Parameter | Recommended Value |
|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 100-300 ft/min (depending on alloy) |
| Tool Material | Carbide for high-strength alloys |
| Coolant | Use flood coolant or air blasts |
| Cutting Tool Type | High-speed steel for softer alloys, carbide for harder alloys |
13. How Do You Maintain Your CNC Machines for Aluminum Machining?
Proper maintenance is critical for ensuring your CNC machines perform at their best when machining aluminum. What’s the real story here? Regular maintenance will help reduce downtime, improve precision, and extend the life of your machines.
First, ensure that your machines are properly cleaned after each machining session. Aluminum chips can clog up essential parts, so keeping your machine free of debris is crucial. But here’s the kicker: regular cleaning is especially important when working with high-strength alloys like 7075, which can cause more chip buildup than softer alloys like 6061.
What about lubrication? Using the right lubricants and oils can help reduce friction and heat during the machining process, leading to smoother operations and reduced tool wear.
Lastly, check for alignment and precision regularly. Even small misalignments can lead to poor results and defects in your parts.
Table: CNC Machine Maintenance Checklist
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean machine | After each use |
| Lubricate moving parts | Monthly |
| Check alignment | Quarterly |
| Inspect cutting tools | After every session |
| Calibrate CNC system | Annually |
14. What Are the Cost Considerations When Machining Aluminum?
Cost is always a concern when it comes to machining aluminum, especially when you’re working with high-performance alloys. What’s the real story here? The cost of aluminum itself is just one factor to consider; machining costs can quickly add up if you’re working with difficult-to-machine alloys like 7075.
The material cost will depend on the alloy you choose. 6061 is generally more affordable than higher-strength alloys like 7075 or 2024. But here’s the kicker: while 7075 may cost more upfront, its higher strength can reduce the need for additional materials or rework in the long run.
Machining costs also vary depending on factors like cutting speed, tool wear, and the need for specialized equipment. To optimize costs, it’s important to balance the need for high-strength materials with the most efficient machining methods.
Table: Aluminum Machining Cost Breakdown
| Factor | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
| Material Cost | Higher for stronger alloys |
| Machining Time | Longer for tougher alloys |
| Tool Wear | Increased for harder alloys |
| Equipment Needs | Specialized tools increase cost |
15. What Are the Future Trends in Aluminum Machining?
As technology continues to evolve, aluminum machining is also undergoing significant changes. This is where it gets interesting: automation, AI, and new machining technologies are revolutionizing the way we work with aluminum.
What’s the catch? While automation and AI can improve efficiency, they also require significant investment. However, the long-term benefits include reduced labor costs, increased production speeds, and improved precision.
What about sustainability? As industries continue to prioritize environmental responsibility, there is a growing focus on reducing waste and improving energy efficiency in aluminum machining. New technologies are emerging that allow for more precise machining, minimizing material waste and energy consumption.
Table: Future Trends in Aluminum Machining
| Trend | Impact on Industry |
|---|---|
| Automation | Reduced labor costs and increased speed |
| AI Integration | Improved precision and efficiency |
| Sustainability | Reduced waste and energy use |
| New Machining Tools | Increased precision and faster production |
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the best aluminum for machining?
The best aluminum for machining depends on the application. 6061 is a versatile choice, but 7075 is ideal for high-strength applications.
Q2: How does aluminum machining differ from machining other metals?
Aluminum is generally easier to machine compared to metals like steel, due to its lower density and superior machinability.
Q3: Why is 6061 aluminum considered the best choice for machining?
6061 aluminum is cost-effective, versatile, and easy to machine, making it ideal for various industrial applications.
Q4: What is the difference between 7075 and 6061 aluminum for machining?
7075 offers superior strength but is harder to machine and more expensive, while 6061 is easier to work with and more affordable.
Q5: How can I improve the quality of my aluminum machining projects?
To improve quality, use the right cutting tools, maintain proper machining parameters, and consider post-machining processes like anodizing.

